We all have habits, some of which are helpful, while others might be harmful without us even realizing it. The key difference between a harmless habit and a harmful addiction often lies in how much control we maintain over our actions. While habits can be beneficial or neutral, addiction takes hold in ways that are difficult to escape.
By exploring the differences between these two behaviors, we can better understand how they shape our actions and when it’s time to seek change, as well as expert help.

What Are Habits and How Do They Form?
A habit is a repetitive behavior that becomes automatic over time. It can start as a simple, conscious action, but with repetition, it becomes a routine. For example, having a glass of water in the morning or exercising after work may seem like intentional acts, but over time, they can become habits.
Each time we repeat a behavior, our brain reinforces it, creating a habit loop. A certain cue triggers the behavior, which in turn provides a reward. This loop solidifies the behavior, making it easier to perform without thinking. In most cases, habits are neutral or beneficial.
For instance, brushing your teeth every morning is a positive habit that improves oral hygiene, whereas smoking is a bad habit that can negatively impact your health.
The Science Behind Habit Formation
Habits are deeply tied to the brain, particularly the basal ganglia, which is involved in forming and reinforcing habits. The habit loop consists of three components: cue, routine, and reward. When a behavior is repeated consistently, the brain automates it, making it a routine part of daily life. This neurological process allows us to perform tasks without much thought, saving mental energy.
For example, when you’re feeling stressed, your brain might prompt you to grab a drink, which serves as a reward. Over time, your brain associates the stress (cue) with drinking alcohol (routine), and the immediate relief it provides (reward) reinforces this pattern. With the right behavioral strategies and consistent effort, these patterns can be reshaped to support healthier, long-term habits.
Characteristics of Habits: Neutral, Beneficial, or Harmful Outcomes
Some habits are helpful, such as exercising, eating healthily, or going to bed on time. Others are neutral, such as checking your phone when you wake up or always using the same mug for coffee – these don’t help or harm you.
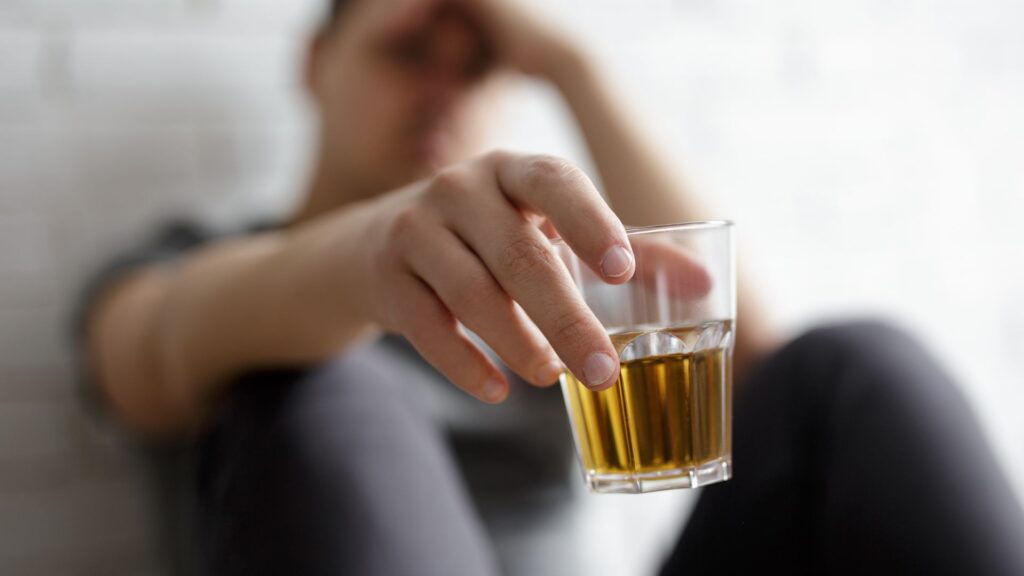
But some habits can be harmful. Smoking, drinking too much, or stress-eating may start small but can lead to serious health problems over time. These unhealthy habits can affect your body, mood, and overall well-being if repeated often enough.
What Is Addiction and How Does It Develop?
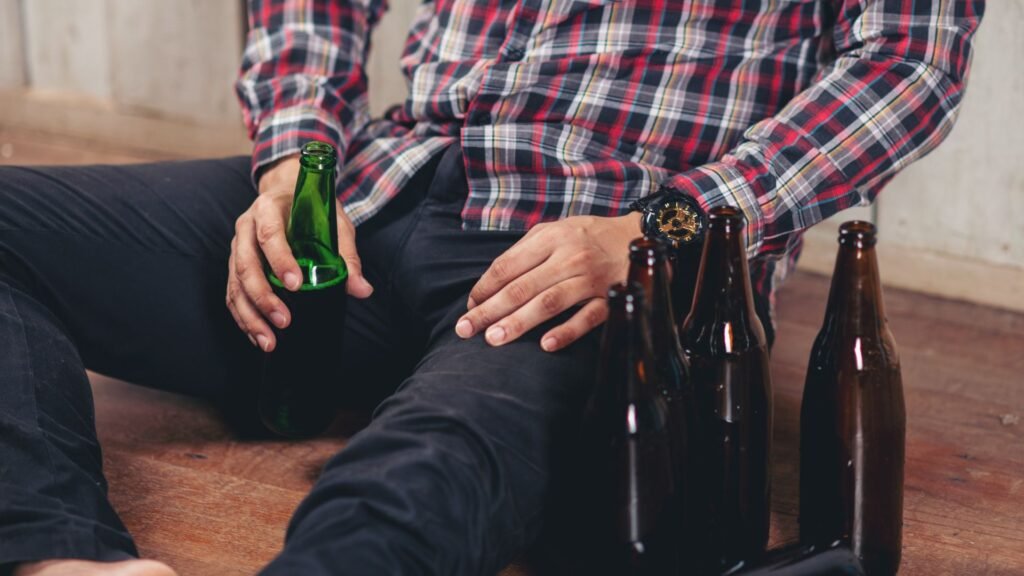
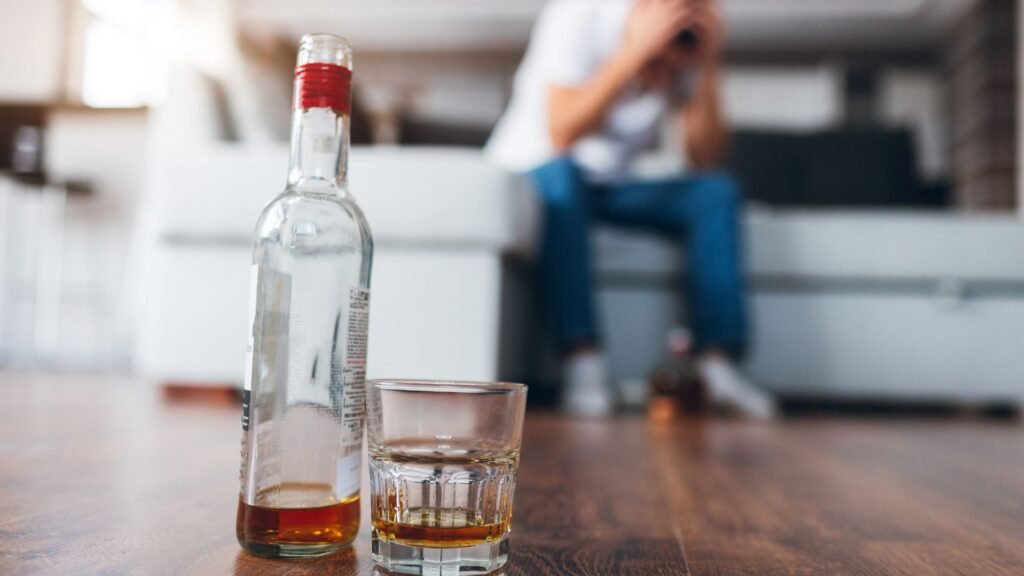
Addiction is a substance use disorder that involves both psychological and physical dependency on a substance or behavior. Addiction doesn’t happen overnight. It typically develops over time, starting with casual use or behavior and gradually becoming a compulsive need. Whether it’s alcohol or drug addiction, repeated use changes the way the brain functions, creating neural pathways that reinforce the addictive behavior.
The key to understanding addiction is recognizing that it is not simply a matter of willpower. Addiction cannot be overcome by simply deciding to stop, it involves a deep, often physical, dependency, which can make it incredibly difficult to break free from. People who are addicted to substances like alcohol or drugs usually experience cravings, withdrawal symptoms, and a powerful urge to repeat the behavior, even if it harms them.
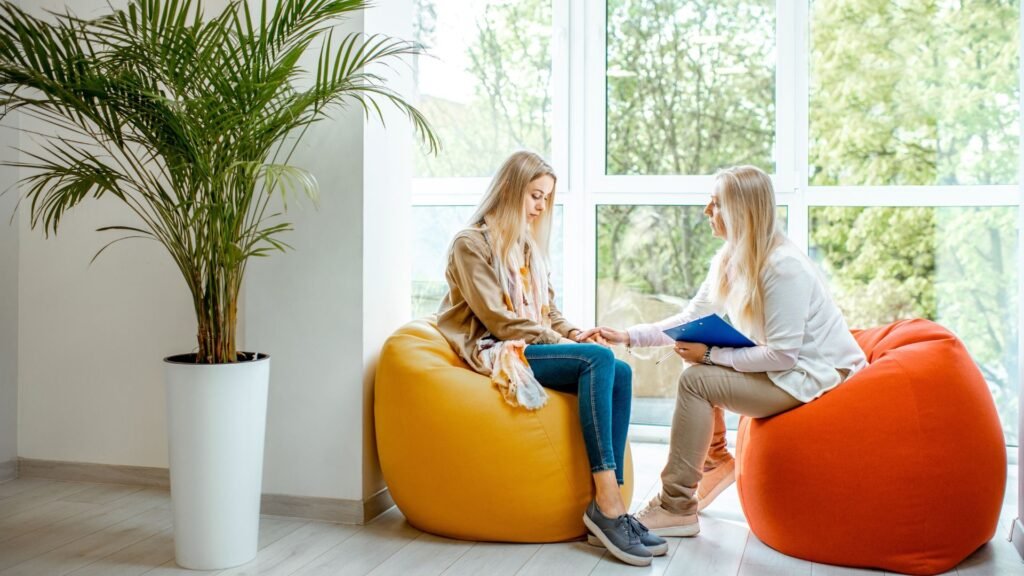
Symptoms of Addiction and Its Impact
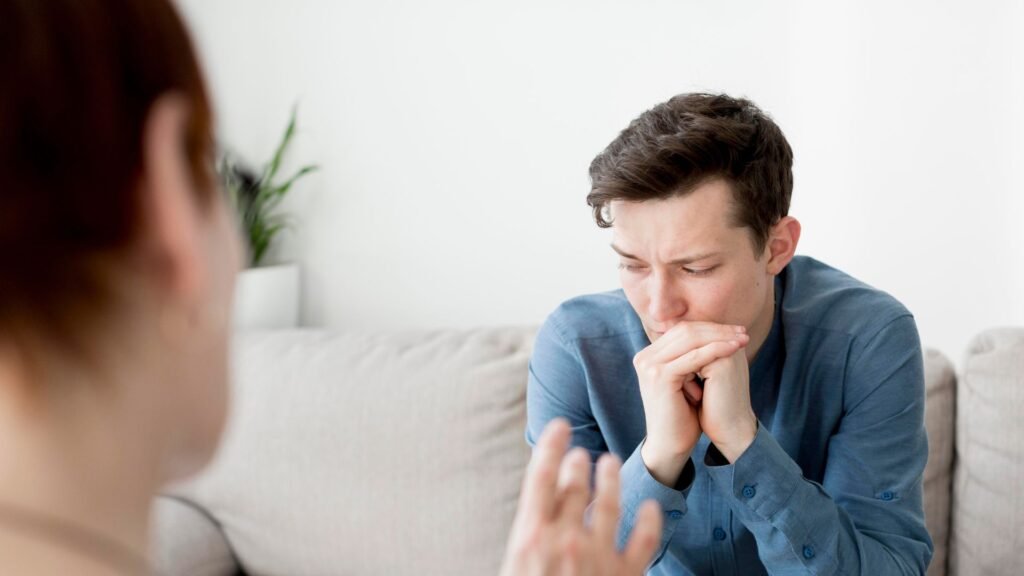
The symptoms of addiction can vary, but they generally include a loss of control over the behavior, an inability to stop despite the desire to quit, and withdrawal symptoms when the behavior or substance is not available. For example, someone trying to quit drinking may experience severe withdrawal symptoms, such as shaking, sweating, or nausea. These physical symptoms can be challenging to manage without proper treatment programs.
The impact of addiction is far-reaching. Not only does it affect the individual’s brain and body, but it also harms relationships, work life, and overall well-being. In severe cases, addiction can lead to depression, trauma, and even legal or financial issues. People struggling with addiction often find themselves trapped in a cycle that feels impossible to break.
Key Differences Between Habits and Addictions
While both habits and addictions involve repetitive behaviors, the key differences are in control, dependency, and consequences. A habit is a behavior that a person can control, and they can often change it consciously. However, an addiction is driven by compulsion and often leads to physical dependency, where the person feels they cannot stop even if they want to.
A critical distinction between habits and addiction is that habits typically don’t cause the same level of suffering or withdrawal symptoms that addiction does. While habits might affect your life in small ways, addiction has a more profound and damaging impact.
Addictions also tend to have a more damaging impact on life, affecting mental health, relationships, and daily functioning. For example, someone addicted to drugs or alcohol may lose their job, face legal trouble, and strain their relationships. In contrast, someone with bad habits, such as biting their nails, is unlikely to experience such severe consequences.
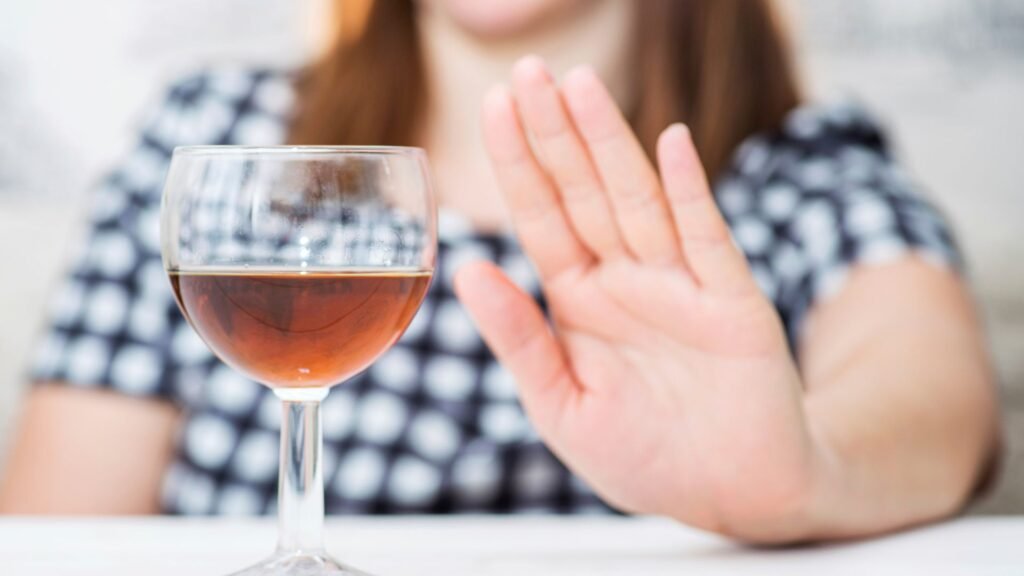
Strategies for Breaking Negative Habits
Breaking a bad habit is possible and often begins with identifying the triggers that cause the behavior. For example, if stress is the trigger for reaching for a drink, practicing stress-relieving techniques like deep breathing or meditation can help redirect that response. Tools like mindfulness and cognitive-behavioral techniques can also help break harmful habits by helping individuals become more aware of their actions and change their behavioral responses.
It’s essential to approach habit change with patience and consistency. Small steps toward change can have a significant impact over time. Setting clear goals and celebrating small successes can also help build motivation to keep moving forward.

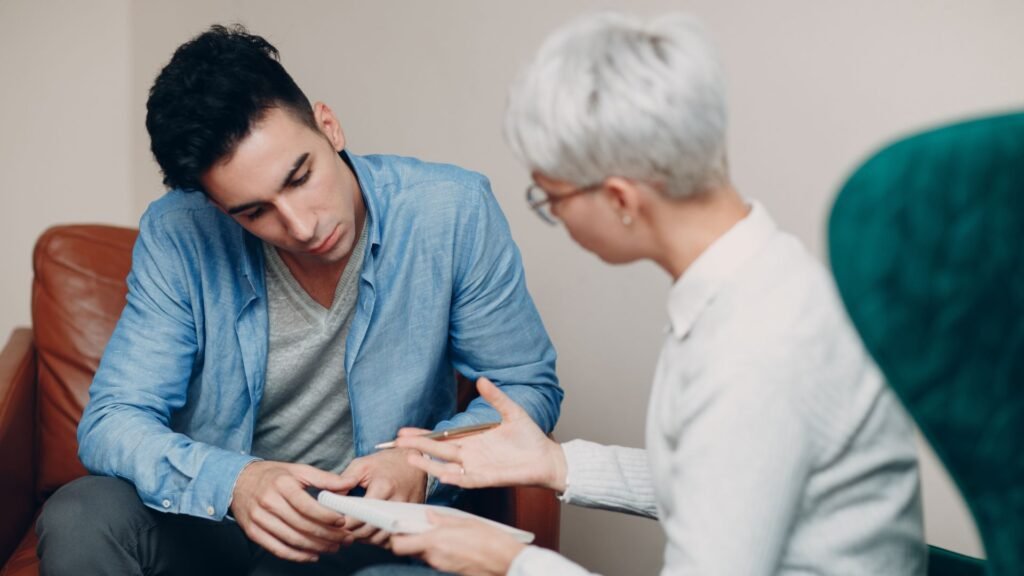
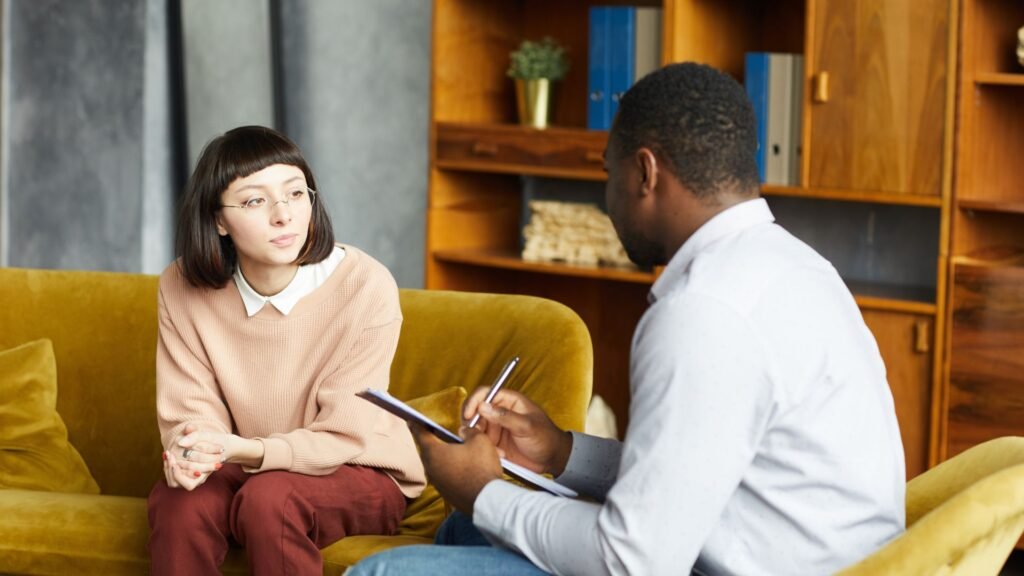
The Importance of Professional Support in Addiction Recovery
While habits can often be changed through personal effort, addiction typically requires specialist intervention. Addiction treatment involves a combination of therapy, counseling, and sometimes medication to address both the psychological and physical aspects of addiction. Integrated treatment approaches are often the most effective, combining therapy, medication, and support groups to help individuals recover from substance abuse.
Professional support is critical in the recovery process. Family and community support also play an essential role in the healing journey. Whether it’s alcohol addiction, drug addiction, or any other type of compulsive behavior, the recovery process can be long and difficult. Still, it’s possible to rebuild a healthier life with proper care.
Final thoughts from Radix Recovery
At Radix Recovery, we acknowledge that while habits can often be managed independently, addictions typically require comprehensive care. Our approach focuses on addressing the underlying factors that contribute to addictive behaviors, providing individuals with the tools and support needed for lasting change. By fostering a compassionate and structured environment, we help individuals transition from harmful patterns to healthier, more fulfilling lifestyles.