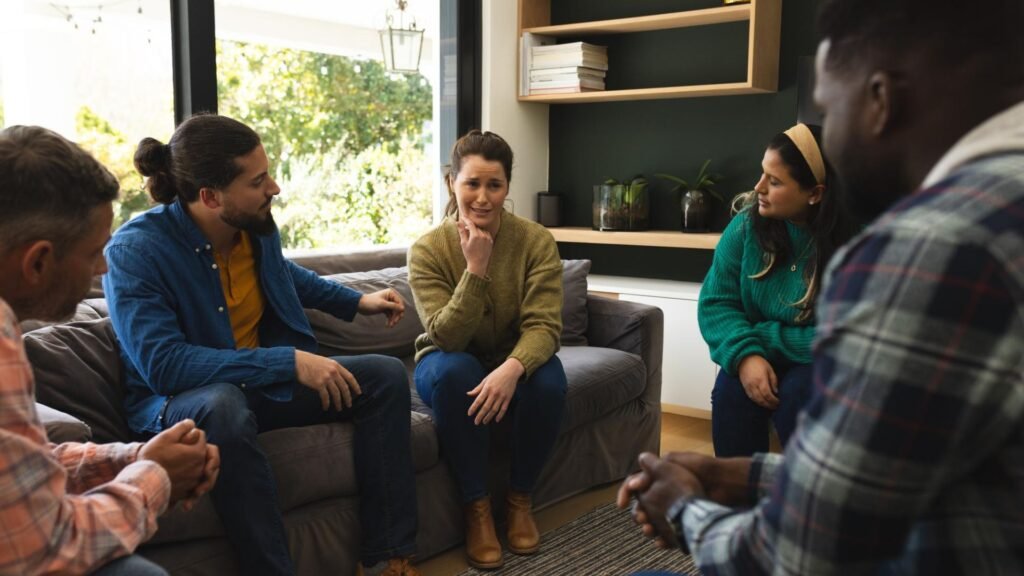
Recognizing the warning signs of Ativan addiction is essential, as this powerful benzodiazepine can quickly lead to dependence and serious health risks, even when taken as prescribed. Recognizing the warning signs of Ativan abuse is crucial for identifying problematic patterns of drug misuse and seeking appropriate help to address the issue before it develops into a more serious issue.
This article will explore the physical, behavioral, psychological, and social warning signs in people struggling with addiction to Ativan, helping readers recognize the early indicators of misuse. Understanding these signs is essential for taking timely action before dependency deepens into a more serious condition.

Understanding Ativan Addiction
Ativan (lorazepam) is a benzodiazepine used to treat anxiety, insomnia, and seizures. It has a known potential for abuse due to its sedative effects, and can lead to physical dependence and psychological addiction when misused.
Ativan addiction treatment involves medically supervised detox, therapy, and sometimes medication. With the right support and care, recovery from Ativan addiction is entirely possible.
If you’re concerned about your use of benzodiazepines or any other substance, taking our self-assessment quiz can help you gain insight into your patterns and determine whether it might be time to seek professional support.
Physical Warning Signs
Tolerance, a hallmark sign of physical dependence, occurs when higher doses are needed to achieve the initial therapeutic effects. When attempting to reduce or discontinue the use of Ativan, people struggling with the drug may experience withdrawal symptoms such as anxiety, insomnia, and tremors, indicating a physical reliance on the medication.
Other observable physical signs of Ativan dependence include drowsiness, dizziness, and impaired coordination, which can interfere with daily functioning and increase the risk of accidents or injuries.
Headaches, fatigue, and changes in appetite are also potential indicators of physical dependence on Ativan.
Behavioral Warning Signs
Using Ativan without a prescription, or in larger amounts or for longer periods than prescribed, is a clear behavioral warning sign of problematic use. Repeated unsuccessful attempts to reduce or control Ativan use also point to an emerging substance use disorder.
As Ativan misuse escalates, a person physically dependent on Ativan may spend increasing amounts of time obtaining, using, and recovering from the drug’s effects. This often leads to neglecting important responsibilities and commitments related to work, school, or family life.
Social isolation and loss of interest in activities once found enjoyable are common as an individual becomes addicted to Ativan. To maintain their supply, some individuals may resort to risky or illegal behaviors such as doctor shopping (visiting multiple prescribers to obtain Ativan) or forging prescriptions. These actions put them at risk for legal consequences and other harms.
Psychological Warning Signs
Psychological addiction is characterized by compulsive, intense cravings, preoccupation with obtaining and using the drug, and relying on it as a primary coping mechanism for stress or emotional discomfort.
Individuals with an Ativan addiction start to experience worsening mental health symptoms, such as increased anxiety, depression, paranoia, or confusion.
Cognitive impairment, including difficulty concentrating, memory problems, and slowed thinking, can also be indicators of Ativan dependence.
Social and Functional Warning Signs
As Ativan abuse takes priority, individuals may begin to isolate themselves, withdrawing from relationships and activities they once enjoyed.
Neglecting responsibilities at work, school, or home becomes more common, potentially leading to job loss, academic failure, or strained personal relationships. Legal problems, such as driving under the influence or engaging in illegal activities to obtain Ativan, can arise from continued misuse.
Financial issues may also occur due to the cost of obtaining the drug or as a result of impaired judgment and decision-making while under the influence. Using Ativan as a primary coping mechanism despite the negative consequences is a strong indicator of a substance use disorder.
Diagnostic Criteria and Professional Assessment
An accurate diagnosis of Ativan addiction requires a professional assessment using the diagnostic criteria outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition, Text Revision (DSM-5 TR). Addiction specialists evaluate the severity of physical dependence, withdrawal symptoms, and other indicators of substance use disorder through a comprehensive evaluation process.
This typically involves a physical examination, psychological assessment, and laboratory tests to gather relevant information about the individual’s health and substance use history.
Based on the findings of the assessment, the addiction specialist can determine if the individual meets the diagnostic criteria for a substance use disorder and recommend appropriate treatment options. Treatment plans are personalized to address the specific needs of the individual, taking into account the severity of their addiction, co-occurring mental health conditions, and other relevant factors.

When and How to Seek Help
Seeking help for an Ativan addiction is an important step in the recovery process. The most effective approach is to consult with a qualified medical professional, such as a primary care physician or addiction specialist, who can evaluate the individual’s specific situation and recommend an appropriate outpatient treatment program.
Treatment options for Ativan addiction may include a medically supervised detoxification process at a treatment center to manage Ativan withdrawal symptoms, behavioral therapies like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or motivational interviewing, and ongoing support through group therapy or 12-step programs.
Research has shown that early intervention can significantly improve the chances of successful recovery from benzodiazepine addiction.
A comprehensive treatment approach that addresses both the physical and psychological aspects of addiction has been found to be more effective than a single treatment modality.
Final Thoughts from Radix Recovery
Recognizing multiple signs of Ativan addiction is a crucial first step toward recovery. At our alcohol and drug rehab center in Cedar Rapids, Iowa, individuals receive comprehensive, structured treatment during the day while still returning home each evening, offering a balanced alternative between inpatient and outpatient care.
Our experienced team at Radix Recovery takes a holistic approach, focusing on uncovering the root causes of addiction, teaching effective coping strategies, and supporting your long-term recovery journey through personalized care.